Generative AI refers to the concept of creating artificial intelligence (AI) that possesses the ability to understand, learn, and perform any intellectual task that a human being can. While we are still far from achieving true Generative AI, Large Language Models (LLMs) represent a significant step forward in this direction. LLMs, such as ChatGPT, are AI systems trained on vast amounts of text data, enabling them to generate coherent and contextually relevant responses to prompts or questions.
The rise of LLMs solutions has sparked widespread interest and debate surrounding their ethical implications. These powerful AI systems, such as GPT-4 and BARD, have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in generating human-like text and engaging in interactive conversations. Unsurprisingly, LLMs are winning people’s hearts and are becoming increasingly popular each day. For instance, GPT-4 has gained tremendous popularity among users, receiving an astounding 10 million queries per day (Invgate). However, like any technology, LLMs and Generative AI in general have their risks and limitations that can hinder their performance and user experience. Moreover, numerous concerns have been raised regarding the Generative AI and LLMs’ challenges, ethics, and constraints. Understanding the risks and limitations of Generative AI and Large Language Models can help in determining future directions for their development.
Table of Contents
Major Risks and Limitations of LLMs and Generative AI Adoption
The rapid progress of Generative AI and natural language processing (NLP) has given rise to increasingly sophisticated and versatile language models. Generative AI models belong to a category of AI models capable of creating new data based on learned patterns and structures from existing data. These models possess the ability to generate content across diverse domains, including text, images, music, and more. Utilizing deep learning techniques and neural networks, Generative AI models analyze, comprehend, and produce content that closely resembles outputs generated by humans (Ray). Among these models, ChatGPT, an AI model developed by OpenAI, has emerged as a powerful tool with wide-ranging applications across various domains.
Through ongoing research, development, and optimization, GPT-4 holds the promise of surpassing other Language Model Models. Already established as one of the most advanced LLMs, GPT-4 exhibits remarkable performance across a wide range of natural language processing benchmarks (Ray). However, to achieve superiority over all other LLMs and maintain its popularity, GPT-4 must persistently enhance its inherent limitations.
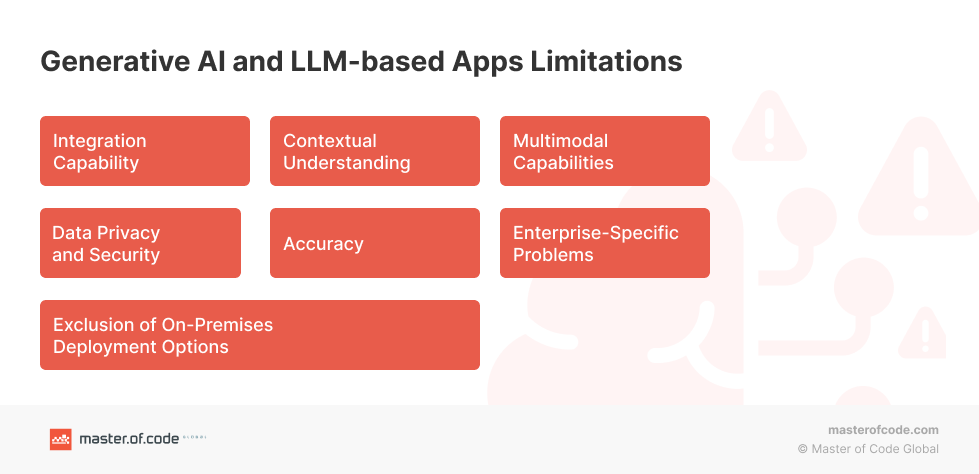
Generative AI and LLM-based Apps Limitation #1: Integration Capability
LLMs, GPT-4 in particular, lacks seamless integration capabilities with transactional systems. It may face difficulties in executing tasks that require interaction with external systems, such as processing payments, updating databases, or handling complex workflows. The limited availability of robust integrations hampers LLMs’ capacity to facilitate seamless end-to-end transactions, thereby diminishing its suitability for eCommerce or customer support scenarios. At the same time, potential of Generative AI chatbots for eCommerce is huge which is reflected in the various use cases. This drawback becomes especially concerning in the realm of customer support, where personalized experiences hold immense importance. According to Startupbonsai, a staggering 80% of customers are more inclined to make purchases from companies that offer tailored experiences and keep them informed with updated account information. Moreover, 43% of customers prefer to speak to a human representative for complex inquiries. As a company specializing in Conversational AI solutions, Master of Code Global envisions the possibility of Generative AI integration into Conversational AI solutions to unlock LLMs potential, improve customer experiences and get GPT-4 to a whole different level.
Generative AI and LLM-based Apps Limitation #2: Contextual Understanding
GPT-4 often struggles to maintain contextual understanding over extended conversations. While it can generate coherent responses within a given context, it may lose track of the conversation’s broader context or fail to remember specific details mentioned earlier. This limitation can lead to disjointed or repetitive interactions, reducing the overall quality of the conversational experience. According to one of the surveys, it was found that approximately 30% of individuals expressed dissatisfaction with their GPT-4 experience, primarily citing incorrect answers or a lack of comprehension (ITSupplyChain).
Generative AI and LLM-based Apps Limitation #3: Multimodal Capabilities
LLMs primarily rely on text-based interactions and lack robust support for other modalities such as images, videos, or audio. It may struggle to interpret or generate responses based on visual or auditory inputs, limiting its effectiveness in scenarios where multimodal communication is crucial. For instance, in industries like fashion or interior design, where visual elements play a significant role, ChatGPT’s inability to process and provide feedback on visual content can be a significant limitation. At Master of Code Global, we stood for omnichannel customer experience, which can be achieved through Conversational AI platform integration with Generative AI, like ChatGPT, bringing personalization and customer experience to a totally different level.
Generative AI and LLM-based Apps Limitation #4: Exclusion of On-Premises Deployment Options
GPT-4 operates exclusively as a cloud-based solution and does not offer on-premises deployment options. Some organizations, particularly those with regulatory or security requirements, prefer to maintain their conversational systems within their own infrastructure. Consequently, ChatGPT’s lack of on-premises deployment may hinder its adoption in companies that mandate self-hosted AI applications, check out an alternative approach of ChatGPT Plugin Development.
Generative AI and LLM-based Apps Limitation #5: Accuracy
While GPT-4 demonstrates impressive language generation, it does not guarantee factual accuracy or real-time information. It generates responses based on patterns and knowledge present in its training data comprising around 570GB of datasets, including web pages, books, and other sources, which nevertheless may not always reflect the most accurate or up-to-date answers (Invgate). This limitation becomes critical in situations where precision and reliability are paramount, such as legal or medical inquiries. Furthermore, according to research conducted by Blackberry, a significant 49% of individuals hold the belief that GPT-4 will be utilized as a means to propagate misinformation and disinformation.
Generative AI and LLM-based Apps Limitation #6: Enterprise-Specific Problems
LLMs’ effectiveness is limited when it comes to addressing enterprise-specific challenges that require domain expertise or access to proprietary data. It may lack knowledge about a company’s internal systems, processes, or industry-specific regulations, making it less suitable for tackling complex issues unique to an organization.
Generative AI and LLM-based Apps Limitation #7: Data Privacy and Security
As a Large Language Model, GPT-4 relies heavily on data access to generate responses. This reliance raises concerns regarding data privacy and security. Based on the research findings from Blackberry, an overwhelming 74% of IT decision-makers not only recognize the potential cybersecurity threat posed by GPT-4 but also express significant concern regarding its implications. Moreover, organizations that handle sensitive customer information or proprietary data may hesitate to utilize a cloud-based AI model like GPT-4 due to potential risks associated with data breaches or unauthorized access. This issue becomes particularly critical in industries like healthcare or banking, where the abundance of personalized data and the accuracy of information make data breaches and other security risks a significant threat to customer identity (Coforge & Startupdaily). Fortunately, OpenAI has been working on this problem, resulting in the introduction of incognito mode to protect user data and further development of a GPT-4 business subscription (SiliconeRepublic).
Understanding the limitations of Generative AI and LLMs in handling transactional tasks, providing accurate information, addressing enterprise-specific problems, restricted deployment options, and data privacy and security concerns emphasizes the importance of exploring specialized Conversational AI platforms tailored to meet specific business requirements. By leveraging Conversational AI platforms, companies can overcome these limitations and create more robust and secure conversational experiences.
Ethical Concerns Surrounding Generative AI and LLMs Use
Large Language Models and Generative AI, such as ChatGPT, have the potential to revolutionize various aspects of our lives, from assisting with tasks to providing information and entertainment. However, their growing capabilities also raise significant ethical concerns. As these models become more prevalent, it is crucial to critically examine the implications they may have on privacy, bias, misinformation, manipulation, accountability, critical thinking, and other important ethical considerations. The list below highlights key concerns surrounding Large Language Models in general and specifically addresses ethical implications related to ChatGPT. Understanding and addressing these concerns is essential to ensure responsible and beneficial use of this powerful technology.

Generative AI and LLMs Adoption Risk #1: Bias and Fairness
Language models are trained on diverse datasets, which can contain biases present in the data sources, which is one of the major concerns in LLMs ethics. This can result in biased outputs or discriminatory behavior by the model, perpetuating societal biases and inequalities. For example, research showed that LLMs considerably over-represent younger users, particularly people from developed countries and English speakers.
Generative AI and LLMs Adoption Risk #2: Misinformation and Disinformation
GPT-4 has the potential to generate misleading or false information. If the model is not guided by strict fact-checking or reliable sources, it may unintentionally propagate misinformation, leading to the spread of inaccurate or harmful content. This LLMs’ ethical concern poses a significant danger, especially for individuals who heavily depend technology in critical domains like Generative AI in healthcare or Generative AI in finance.
Generative AI and LLMs Adoption Risk #3: Manipulation and Deception
Large language models can be used to manipulate or deceive individuals. For example, they can be employed in phishing attacks or social engineering schemes, impersonating trusted entities to deceive users into sharing sensitive information.
Generative AI and LLMs Adoption Risk #4: Lack of Accountability
As language models become more sophisticated, it becomes challenging to attribute responsibility for the actions or outputs of the model. This lack of accountability raises concerns about potential misuse and the inability to hold individuals or organizations accountable for any harm caused.
Generative AI and LLMs Adoption Risk #5: Overreliance and Loss of Critical Thinking
If individuals rely heavily on language models like GPT-4 for information or decision-making, there is a risk of diminishing critical thinking skills. Blindly accepting the model’s responses without critical evaluation could lead to a loss of independent judgment and reasoning. One of the examples is the use of GPT-4 by students to complete assignments, which is considered cheating and has led to blocking of GPT-4 by various schools to “protect academic honesty”.
Generative AI and LLMs Adoption Risk #6: Intellectual Property and Plagiarism
Language models have the ability to generate creative content, raising questions about intellectual property rights and plagiarism. Determining the originality of the generated content and establishing appropriate attribution becomes a challenge in such scenarios.
Generative AI and LLMs Adoption Risk #7: Psychological and Emotional Impact
Interacting with language models like GPT-4 might have psychological and emotional implications, especially for vulnerable individuals. Dependence on machine-generated companionship or advice could impact human relationships and well-being.
It is important to address these concerns through ongoing research, responsible development, transparency, and the implementation of appropriate guidelines and regulations to ensure the ethical use of Large Language Models.

Future Potential: Integrating Conversational AI Platforms with LLMs and Generative AI
Generative AI and Large Language Models have made significant strides in natural language processing, opening up new possibilities across various domains. However, they still possess certain limitations that hinder their full potential. Fortunately, the integration of Conversational AI platforms with these technologies offers a promising solution to overcome these challenges. At Master of Code Global we believe that by seamlessly integrating Conversational AI platforms with GPT technology, one can unlock the untapped potential to enhance accuracy, fluency, versatility, and the overall user experience.
- Improved Contextual Understanding: Generative AI and LLMs are proficient in processing and generating text, but they often struggle with context. Conversational AI platforms, on the other hand, excel at understanding and maintaining context within a conversation. By integrating Conversational AI platforms with Generative AI and LLMs, we get Generative AI Chatbots that gain the ability to maintain context over extended dialogues, resulting in more coherent and relevant responses.
- Dynamic Interaction: One of the key challenges with Generative AI and LLMs is their limited capability to engage in dynamic conversations. Conversational AI platforms provide the necessary infrastructure to create interactive experiences. Whereas, Generative AI Chatbots become capable of dynamic back-and-forth exchanges, making interactions with AI models feel more human-like and engaging.
- Personalization and Customization: Generative AI and LLMs often lack the ability to adapt to individual preferences and personalize responses. Conversational AI platforms offer user profiling and customization features that can enhance the output of the AI models. Generative AI Chatbots, on the other side, can learn from user interactions, understand preferences, and tailor responses accordingly, leading to more personalized and relevant conversational experiences.
- Content Filtering and Control: Concerns around content filtering and control arise when using Generative AI and LLMs in various applications, such as customer support or content moderation. Conversational AI platforms provide robust moderation and filtering mechanisms, allowing administrators to control the output and ensure compliance with guidelines. This integration ensures a safer and more responsible use of AI models in real-world scenarios.
- Natural Language Generation: LLMs excel in generating coherent and contextually appropriate text, but they often struggle with generating structured content, such as reports, summaries, or product descriptions. Conversational AI platforms, which incorporate Natural Language Generation (NLG) capabilities, can enhance the structured output of LLMs. By leveraging the NLG features of Conversational AI platforms, Generative AI Chatbots can produce more structured and concise text, thereby improving the overall quality of the generated content.
Key Takeaways
The integration of Conversational AI platforms with Generative AI and LLMs offers immense potential in overcoming limitations associated with these technologies. With the brand-new Embedded Generative AI model developed by Master of Code experts, any existing bot project can be upgraded to leverage Natural Language Generation technology and Generative AI Chatbots capabilities. Whether it’s customer support, retail sales, information services, consulting, or system queries, our solution delivers maximum outcomes at the lowest possible cost.
Notably, renowned conversational AI platforms like Replika AI, Haptik, BotStar, and Botpress have already embraced OpenAI’s GPT technology. By harnessing the power of Conversational AI platforms, we can enhance contextual understanding, dynamic interaction, personalization, content filtering, and natural language generation. This integration unlocks exciting possibilities across domains like customer support, content generation, virtual assistants, and more. As AI continues to evolve, we are moving closer to a future where our software becomes an indispensable part of daily life. Join us and experience the transformative potential of our advanced conversational AI solution.
Don’t miss out on the opportunity to see how Generative AI chatbots can revolutionize your customer support and boost your company’s efficiency.